Owner-occupied households most Environmentally Aware, according to new CSO figures

March 14th, 2016
The Central Statistics Office (CSO) today released the results of the Quarterly National Household Survey module on Household Environmental Behaviours. The survey examined behaviours related to energy use, energy efficiency, waste disposal and environmental awareness.
Environmental Awareness
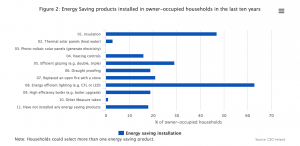
Owner-occupied households with children were found to be most environmentally aware. They were most likely to be aware of the environmental initiatives Green Schools, Green Homes and Stopfoodwaste.ie. The highest proportion (22%) of owner-occupied households were fully influenced by the energy-efficiency rating when purchasing large electrical items, compared to 12% of those living in rented accommodation, and they were also most likely to have installed energy efficient lighting (63%), insulation (48%) and better glazing (29%) in the last 10 years.
Heating and Washing
Natural gas was found to be the main heating fuel in 35% of households. A stark contrast was observed between those who used it as their main fuel in Dublin (72%) and those who did so in the West of Ireland (5%). Peat remains the primary heating fuel for many households in the Midlands (34%) and in the Western Region (24%). This discrepancy was partly attributed to differences in the availability of the gas distribution network. As for supplementary heating on a fire or stove, coal (28%) was the most popular fuel followed by the more sustainable wood logs (23%). Almost half of Irish households (49%) reported using a power shower every day, whereas the method of heating water for taps varied seasonally. In Winter, 82% of houses reported using central heating to heat their water, whereas in summer time immersion heating had become the primary source, at 52% of households.
Transport
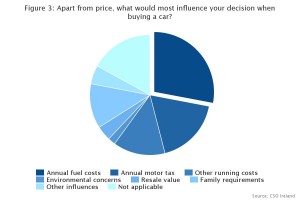 Despite transport contributing 29% of Ireland’s non-Emissions Trading Scheme (non-ETS) emissions, a mere 2% of respondents responded that, after price, the emissions of a vehicle was an important factor to them in the purchase of a new vehicle. Fuel costs and motor tax featured more frequently as the second highest concern.
Despite transport contributing 29% of Ireland’s non-Emissions Trading Scheme (non-ETS) emissions, a mere 2% of respondents responded that, after price, the emissions of a vehicle was an important factor to them in the purchase of a new vehicle. Fuel costs and motor tax featured more frequently as the second highest concern.
Recycling and Waste Reduction
There was a clear urban/rural divide in mode of recycling, with 24% of rural dwellers bringing their recycling to a recycling centre compared to only 6% of urban dwellers doing so. The most popular waste reduction measure that was practiced relates to food waste reduction: an impressive 51% of respondents claimed to only buy products that can be used by the sell-by date. While there are also obvious cost implications of buying food with the longest sell-by date, a consequence of taking this practice to extremes can be that it actually leads to more waste at shop level. A sizeable portion of the Irish public (35%) claimed to choose products will less packaging as a waste reduction measure.
Commenting on the results Mr. Dara Lynott, Director, EPA Office of Environmental Sustainability said:
“This publication provides valuable and comprehensive information on people’s attitudes and behaviours regarding waste management, energy use and purchasing behaviour. It will inform EPA work across a number of areas, such as waste prevention, hazardous waste management planning, air quality and statistical reporting obligations.” Responses were obtained from 13,032 households, which were selected to be nationally representative.
[x_button shape=”square” size=”regular” float=”none” href=”http://www.cso.ie/en/releasesandpublications/er/q-env/qnhsenvironmentmoduleq22014/” info=”none” info_place=”top” info_trigger=”hover”]Click here to read the CSO statistics on Household Environmental Behaviours[/x_button]
[x_author title=”About the Author”]